TLDR
-
On January 28, 2026, the Bank of Canada announced that it is holding its interest rate at 2.25%.
-
Changes in the Bank of Canada’s policy rate can impact your mortgage, influencing both your monthly payments and long-term financial planning.
-
Every situation is unique so you may want to speak with a mortgage advisor who can advise you on the right mortgage solution for you.
-
The next Bank of Canada interest rate announcement is Wednesday, March 18, 2026.
Whether you’re looking to purchase a home, renew your existing mortgage or want to add a unit to your property, an RBC Mortgage Specialist can advise you on the right mortgage solution for your situation.
How Rates Have Changed Over the Last 12 Months
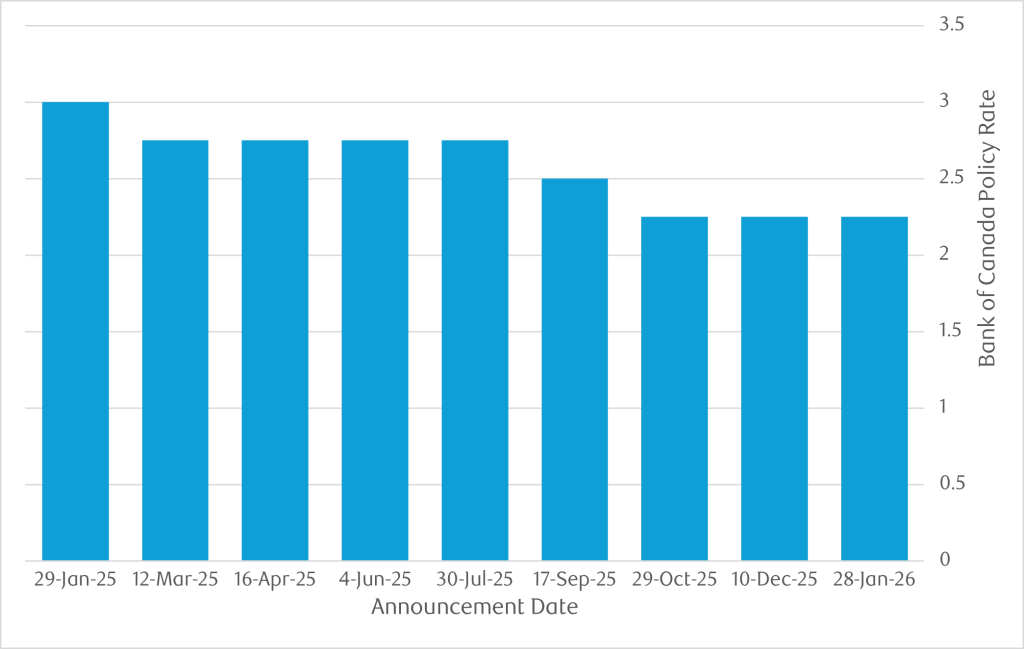
| Announcement Date | Bank of Canada Policy Rate (%) | Change (%) |
| 28-Jan-26 | 2.25 | — |
| 10-Dec-25 | 2.25 | — |
| 29-Oct-25 | 2.25 | -0.25 |
| 17-Sep-25 | 2.5 | -0.25 |
| 30-Jul-25 | 2.75 | — |
| 4-Jun-25 | 2.75 | — |
| 16-Apr-25 | 2.75 | — |
| 12-Mar-25 | 2.75 | -0.25 |
| 29-Jan-25 | 3.00 | -0.25 |
The Bank of Canada’s policy rate, also known as the overnight rate, plays a critical role in shaping the financial landscape of the country. It directly influences borrowing costs, including mortgage rates, and can have a significant impact on homeowners and prospective buyers. Understanding how changes in the policy rate affect your mortgage is essential for managing your finances effectively.
What is the Bank of Canada Policy Rate?
The policy rate is the interest rate at which major financial institutions borrow and lend money to each other overnight. The Bank of Canada adjusts this rate to achieve its monetary policy goals, such as controlling inflation, stabilizing the economy, and fostering employment growth. When the policy rate changes, it sets off a chain reaction that affects various interest rates across the economy, including those tied to mortgages.
Impact on Variable-Rate Mortgages
If you have a variable-rate mortgage, changes in the Bank of Canada’s policy rate could directly affect your mortgage payments. Variable-rate mortgages are tied to a lender’s prime rate, which typically moves in tandem with the policy rate. It is important that you speak with your Mortgage Specialist to understand the type of mortgage you have and what triggers could be activated by a rate change as these vary by lender.
-
Rate Increase: When the Bank of Canada raises the policy rate, your lender’s prime rate will likely increase as well. This means your mortgage interest rate will rise and depending on the type of variable rate mortgage you could either have:
-
the same monthly payment. This occurs in most cases with RBC, so can be sure how much your payment will be each month. However, you’d be repaying less towards the principle therefore extending the time it’ll take to pay off your mortgage.
-
higher monthly payments – that you would need to plan for.
-
-
Rate Decrease: Conversely, if the Bank of Canada lowers the policy rate, your lender’s prime rate will likely decrease. With RBC, your mortgage payment will remain the same, but a reduction in your mortgage interest rate would mean that more of your payment is being allocated to paying off the principle and could reduce the time it takes to pay off your mortgage.
Impact on Fixed-Rate Mortgages
For fixed-rate mortgages, the effect of changes in the policy rate is less immediate but still significant. Fixed-rate mortgages are influenced by bond yields, which are indirectly affected by the policy rate.
-
Rate Increase: When the policy rate rises, bond yields often increase as well, leading to higher fixed mortgage rates. This means that if you’re renewing your mortgage or applying for a new one, you could face higher interest rates, resulting in larger monthly payments.
-
Rate Decrease: A lower policy rate can lead to lower bond yields, which may reduce fixed mortgage rates. This could make fixed-rate mortgages more affordable for new buyers or those renewing their loans.
Broader Implications
Changes in the policy rate can also affect housing affordability and the overall real estate market. Higher rates can cool down housing demand, as borrowing becomes more expensive, potentially leading to slower price growth or even price declines. On the other hand, lower rates can stimulate demand, driving up home prices.
How to Prepare for Rate Changes
-
Budget for flexibility: If you have a variable-rate mortgage, ensure your budget can accommodate potential rate increases.
-
Consider fixed vs. variable: Evaluate whether a fixed-rate mortgage might provide more stability in a rising rate environment.
-
Stress-test your finances: Use a higher hypothetical interest rate to assess whether you can still afford your mortgage payments if rates rise.
-
Stay informed: Keep an eye on economic indicators and announcements from the Bank of Canada to anticipate potential rate changes.
Changes in the Bank of Canada’s policy rate can impact your mortgage, influencing both your monthly payments and long-term financial planning. Whether you have a variable or fixed-rate mortgage, understanding these dynamics can help you make informed decisions and navigate the evolving economic landscape.
Ready to have a conversation?
Your mortgage could be a powerful financial tool – make sure it’s working for you. Call 1-866-245-6737 or speak with an RBC Advisor today
Your Top Questions on Bank of Canada Interest Rate Answered
The Bank of Canada (BoC) is Canada’s central bank that has been in operation since 1935. Unlike regular banks offering personal banking services such as opening an account, the primary role of a central bank is to help build a stable economy and the financial well-being of Canadians.
The BoC manages the country’s monetary policy, sets the interest rate and controls inflation. It also issues Canadian banknotes, manages foreign exchange reserves and supports a stable Canadian dollar in the global market.
The Bank of Canada’s interest rate policy is primarily about inflation-control and price stability to sustain economic growth. This is done by adjusting the policy interest rate (called overnight rate) to a targeted range of 2%, so that prices don’t rise or fall sharply.
-
When inflation is high, the Bank may raise rates to make borrowing expensive and slow down spending.
-
When the economy is weak, the Bank lowers rates to make borrowing affordable and boost spending.
Prime Rate: The prime rate is the annual interest rate that financial institutions use to determine the rates they charge for variable mortgage loans, lines of credit and other financial products. It its influenced by the Bank of Canada target for overnight rate, which is the rate at which banks lend to each other. When the Bank of Canada changes its policy rate, banks adjust their prime lending rates which impact the interest rates on your loan products.
For example: a higher prime rate may result in a higher interest rate on your mortgage loan. A lower prime rate can bring down your mortgage interest rate, so homes become more affordable in that period.
Interest Rate: This refers to the cost of borrowing money, usually measured in percentage. There are different types of interest rates:
-
Bank of Canada’s Policy Rate: the central rate that influences the economy.
-
Prime Rate: A type of interest rate that banks use
-
Fixed mortgage rate: a specific interest rate locked in for the term of a loan
-
Credit card interest rate: usually fixed and higher.
The BoC updates its key interest rate about 8 times a year (January, March, April, June, July, September, October and December.) The dates are predetermined by the Government Council after reviewing current economic conditions, inflation and growth prospects. The interest rate decision to raise, lower or hold the rate is typically announced the day after the decision is made.
The BoC interest rate can directly affect your mortgage payments, depending on your mortgage type.
-
Variable-Rate Mortgage: The rate change immediately impacts your payments.
If the interest rate and monthly payment increases, you may need to pay more for your mortgage interest too. When rates go down, your payments can drop, saving you money.
-
Fixed-Rate Mortgage: Future impact when you renew.
Your rate stays the same until the end of your term, even if the BoC rate changes. However, new fixed rates are influenced by bond markets, which are impacted by BoC changes. When you renew, switch or buy a new home, the rate you are offered might be higher or lower, depending on the rate change then. Find out more
The Bank of Canada announces its interest rate decisions at 09:45 ET on scheduled dates. A press conference with the Governor typically follows at approximately 10:30 ET.
When is the next Bank of Canada interest rate announcement?
Staying up to date on the interest rate environment can help you make informed mortgage decisions – and prepare for any adjustments needed to stay on track with your homeownership and financial goals.
The next Bank of Canada interest rate announcement is Wednesday, March 18, 2026.






